Service
A Service is an abstraction of an API (which can also be understood as a set of Route abstractions). It usually corresponds to the upstream service abstraction. Between Route and Service, usually the relationship of N:1, please see the following image.
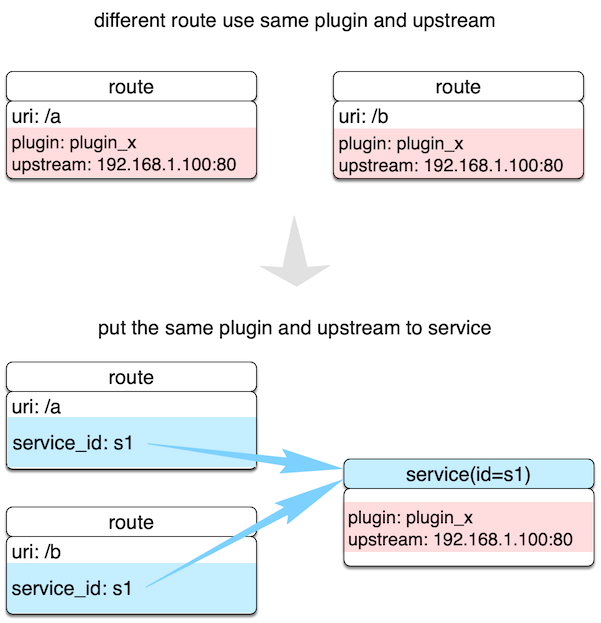
Different Route rules are bound to a Service at the same time. These Routes will have the same upstream and plugin configuration, reducing redundant configuration.
The following example creates a Service that enables the current-limit plugin, and then binds the Route with the id of 100 and 101 to the Service.
# create new Service$ curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/services/200 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '{ "plugins": { "limit-count": { "count": 2, "time_window": 60, "rejected_code": 503, "key": "remote_addr" } }, "upstream": { "type": "roundrobin", "nodes": { "39.97.63.215:80": 1 } }}'
# create new Route and reference the service by id `200`curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/100 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '{ "methods": ["GET"], "uri": "/index.html", "service_id": "200"}'
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/101 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '{ "methods": ["GET"], "uri": "/foo/index.html", "service_id": "200"}'Of course, we can also specify different plugin parameters or upstream for Route. Some of the following Routes have different current-limit parameters. Other parts (such as upstream) continue to use the configuration parameters in Service.
curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/102 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '{ "uri": "/bar/index.html", "id": "102", "service_id": "200", "plugins": { "limit-count": { "count": 2000, "time_window": 60, "rejected_code": 503, "key": "remote_addr" } }}'Note: When both Route and Service enable the same plugin, the Route parameter has a higher priority than Service.